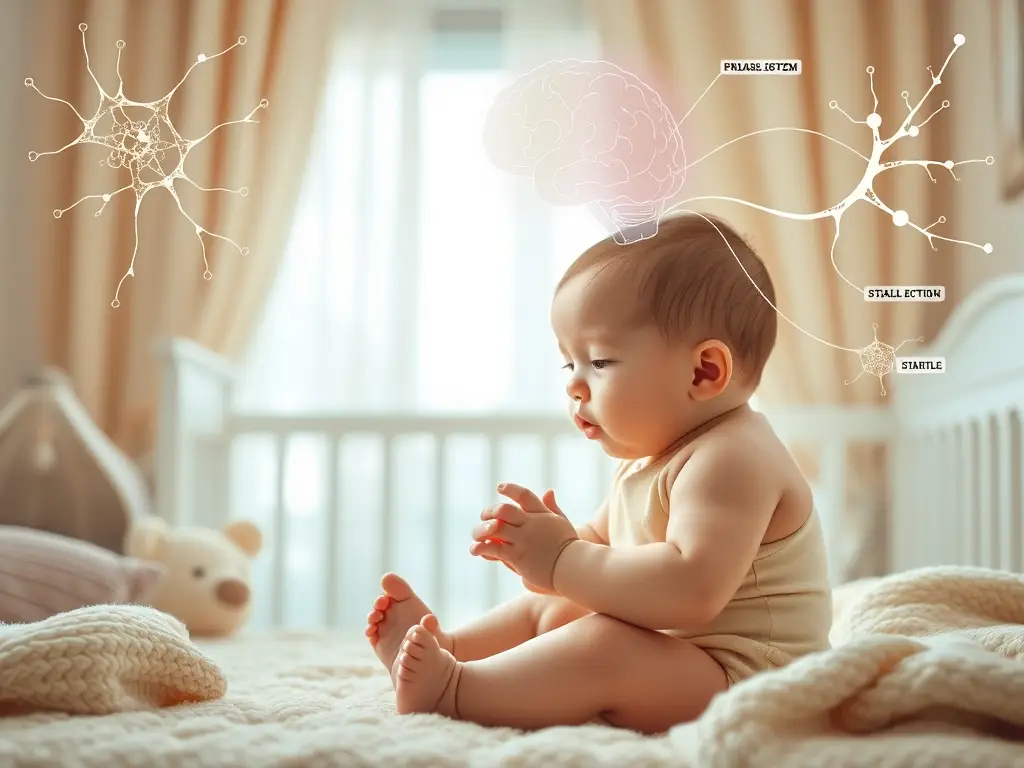
In a world filled with distractions, helping our children develop their focus is a crucial skill. For those navigating the challenges of ADHD, Autism, Dyslexia, or other developmental delays, enhancing focus becomes even more vital. Fortunately, there are transformative neurodevelopmental exercises that can pave the way for improved concentration and cognitive abilities in children.
Understanding Neurodevelopmental Exercises
Neurodevelopmental exercises are more than just physical movements; they are targeted activities designed to stimulate specific neural pathways and enhance brain connectivity. These exercises are rooted in the concept of neuroplasticity, the brain’s remarkable ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections throughout life.
Neuroplasticity and Brain Rewiring
The brain’s structure and function can adapt and change in response to experiences, environmental influences, and activities. This ability, known as neuroplasticity, plays a pivotal role in learning, memory, and skill development.
Neurodevelopmental exercises use neuroplasticity to engage various parts of the brain simultaneously. They trigger the brain’s ability to rewire and reorganize itself, forming new neural networks and strengthening existing connections. As children engage in these exercises, they stimulate specific neural pathways associated with attention, focus, and cognitive processing.
Activation of Brain Hemispheres
Many neurodevelopmental exercises, such as cross-crawl movements and brain gym activities, encourage the integration of both brain hemispheres. This connection is crucial as it fosters communication between the left and right sides of the brain, promoting brain function.
The coordination required in these exercises activates the corpus callosum, the bundle of nerve fibers connecting the brain’s hemispheres. Through this activation, information flows more freely between different brain regions, facilitating improved coordination, focus, and cognitive abilities.
Sensory Stimulation and Brain Development
Sensory integration plays a huge role in neurodevelopmental exercises. When children engage in sensory play (activities that involve multiple senses), they stimulate various sensory pathways in the brain. These sensory inputs are processed and integrated, contributing to a more organized sensory system.
This integration is essential, especially for children with sensory processing difficulties. By engaging in sensory activities, the brain learns to regulate and process sensory information more effectively, leading to improved attention and focus in different environments.
The Role of Mindfulness and Breathing
Mindfulness practices and breathing exercises have shown remarkable effects on brain function. They activate the parasympathetic nervous system, triggering relaxation responses in the brain.
Research indicates that regular mindfulness practices can lead to structural changes in the brain, particularly in areas associated with attention and emotional regulation. By promoting a calmer, more focused state of mind, mindfulness exercises complement other neurodevelopmental activities, optimizing the brain’s capacity for sustained attention and focus.
In summary, neurodevelopmental exercises use the brain’s plasticity to create new neural connections, enhance communication between brain regions, and refine sensory processing. These exercises offer an approach to reshaping brain connectivity and fostering improved focus and cognitive abilities in children.
Neurodevelopmental Exercise #1: Brain Gym Activities
Brain Gym activities are designed to stimulate brain function and enhance cognitive abilities. These movements involve cross-body coordination and specific patterns that activate key brain regions associated with attention and focus.
Exercise Ideas:
Cross Crawl: This classic exercise involves touching the right elbow to the left knee while simultaneously walking, then alternating to the left elbow and right knee. Encourage your child to perform this movement pattern rhythmically for several minutes.
Lazy 8s: Draw large figure-eight shapes in the air using one hand, then switch to the other hand. This activity promotes bilateral coordination and stimulates the brain’s visual-motor connections.
Neurodevelopmental Exercise #2: Rhythmic Movement Patterns
Rhythmic movement exercises involve repetitive and rhythmic patterns that engage large muscle groups in a coordinated manner. These movements are particularly effective in stimulating the brainstem and cerebellum, areas crucial for coordination, balance, and overall brain function.
Exercise Ideas:
Marching with Arm and Leg Coordination: Have your child stand upright and lift their right knee while simultaneously raising their left arm. Alternate this movement by lifting the left knee and right arm. Encourage them to maintain a steady rhythm, focusing on coordination between limbs.
Crossing the Midline with Toe Touches: Ask your child to stand with feet shoulder-width apart. Instruct them to bend at the waist and touch their right hand to their left foot, then switch to touch their left hand to their right foot. Repeat this cross-body movement pattern.
Skipping or Galloping: Engage your child in skipping or galloping movements, which involve coordinated leg and arm movements while maintaining a rhythmic pattern. These activities encourage synchronization and balance while stimulating brain regions associated with coordination and focus.
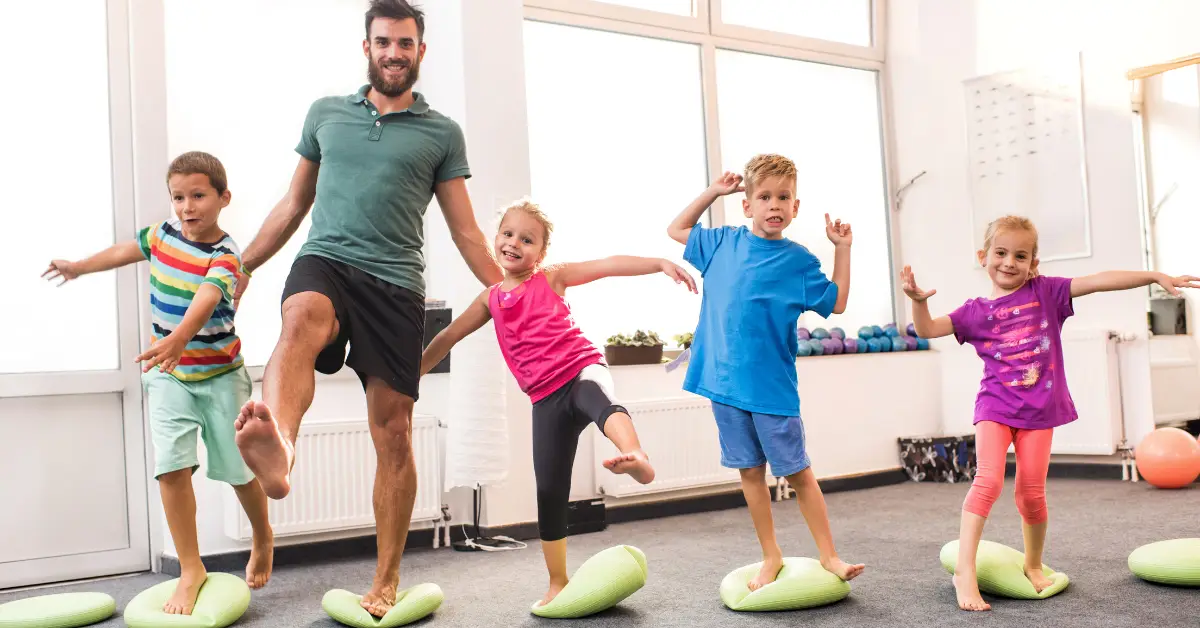
Neurodevelopmental Exercise #3: Balancing Acts
Balancing exercises, such as standing on one foot or walking along a straight line, engage the brain’s proprioceptive senses. This engagement helps in refining spatial awareness and concentration, contributing to better focus and stability in daily tasks.
Exercise Ideas
One-Leg Stand: Start with a basic balancing exercise. Have your child lift one foot off the ground and maintain balance for a few seconds. Encourage them to switch legs and gradually increase the duration of the balance hold as their stability improves.
Tightrope Walk: Create an imaginary tightrope on the floor using tape or draw a line. Ask your child to walk along the line, placing one foot directly in front of the other to simulate walking on a tightrope. This exercise promotes focus and balance.
Balance Board or Cushion: Utilize a balance board or a cushion to challenge your child’s stability further. Have them stand on the board or cushion while maintaining balance. This exercise engages core muscles and promotes stability.
Neurodevelopmental Exercise #4: Sensory Integration Play
Engaging in sensory play, like playing with textured materials or engaging in activities that involve different sensory inputs (sight, touch, sound), can aid in regulating sensory processing. This regulation contributes to better attention and focus in various environments.
Exercise Ideas:
Texture Exploration: Provide various textured materials like sand, rice, or playdough for tactile exploration. Encourage your child to feel and manipulate these textures, fostering tactile awareness and sensory stimulation.
Sensory Bins or Boxes: Create sensory bins filled with items like dried beans, beads, or textured objects. Ask your child to search for specific items or simply explore the sensory contents, engaging their senses of touch and sight.
Sound Exploration: Introduce musical instruments, shakers, or objects with different sounds. Encourage your child to explore and create sounds, fostering auditory stimulation and sensory processing.
Sensory Walk or Obstacle Course: Set up an obstacle course with various textures and sensory experiences. Include surfaces like grass, sand, or mats for different tactile sensations. Incorporate activities that require crawling, jumping, or balancing to engage multiple senses.
Neurodevelopmental Exercise #5: Mindfulness and Breathing Techniques
Practicing mindfulness and simple breathing exercises can significantly impact focus. Encourage your child to take a few moments daily to focus on their breath, fostering a calmer mind that’s better equipped to concentrate on tasks.
Exercise Ideas:
Deep Belly Breathing: Encourage your child to lie down or sit comfortably. Instruct them to place one hand on their chest and the other on their belly. Ask them to take slow, deep breaths, feeling their belly rise and fall with each breath. This technique promotes relaxation and a calmer state of mind.
5-4-3-2-1 Grounding Technique: Guide your child through a sensory grounding exercise. Ask them to name five things they see, four things they feel, three things they hear, two things they smell, and one thing they taste. This exercise helps anchor attention to the present moment.
Mindful Listening: Practice mindful listening by focusing on environmental sounds. Sit quietly with your child and pay attention to various sounds around you, without judgment or analysis. This exercise enhances auditory awareness and cultivates a sense of presence.
Body Scan Meditation: Guide your child through a body scan meditation. Start from the top of the head and slowly move attention down the body, noticing sensations in each body part. This practice promotes relaxation and body awareness.
Neurodevelopmental Exercise #6: Visual Tracking and Coordination
Visual tracking exercises help improve eye movement control and coordination, essential for reading, attention, and overall cognitive function.
Exercise Ideas:
Tracking with Moving Objects: Use various visual tracking tools like a flashlight, a bouncing ball, or an object suspended on a string. Ask your child to visually track the movement of the object while keeping their head still. Start with slow, predictable movements and gradually increase the complexity by introducing irregular patterns or faster movements.
Maze and Puzzle Activities: Provide your child with mazes, puzzles, or activity books that require tracking lines or sequences. Encourage them to trace lines or solve puzzles that involve following a path or sequence, fostering eye coordination and attention to detail.
Reading Aloud with a Finger Guide: While reading together, have your child use their finger or a marker to guide their eyes along the lines of text. This simple action helps in maintaining focus and improving eye movement control while reading.
Final Thoughts
Incorporating these neurodevelopmental exercises into your child’s routine can yield profound improvements in focus and attention. Remember, consistency and patience are key. Celebrate small victories along the way, and embrace these exercises as opportunities for connection and growth with your child.
By nurturing their developing brains through these exercises, you’re empowering them to navigate the world with newfound clarity and focus, setting the stage for a brighter, more focused future.
At NeuroFiT Connections, we specialize in providing tailored neurodevelopmental exercises along with personalized nutrition coaching to support your child’s holistic development. Discover how our specialized programs can empower your child to thrive and reach their full potential.